Notes on Personal Finance
These notes are from books:
- I Will Teach You to Be Rich by Ramit Sethi
- Let’s Talk Money: You’ve Worked Hard for It, Now Make It Work for You by Monika Halan
- Start investing as early as possible.
- Investing isn’t about picking stocks. There is a difference between trading and investing.
Conscious Spending
- Spend extravagantly on the things you love and cut costs mercilessly on the things you don’t. This is called Conscious Spending; spending with a plan.
- A Conscious Spending Plan involves three major buckets where your money will go: fixed costs, investments & savings, and guilt-free spending money.
| Fixed cost (Rent, utilities, debt, etc.) |
45–50% of take-home pay |
| Guilt-free spending money (Dining out, drinking, movies, clothes, shoes, etc.) |
20-35% |
| Investments and saving goals (PPF, FDs, buying a house etc.) |
20-25% |
- Build cash flow system. Use 3 bank account(income account, spent-it, invest-it)
- Use zero balance account for income account.
- Transfer money to spent-it account for all the expenditure.
- Spending on living costs should be less than 45-50 % of take-home income.
- Calculating expenditure :
- Add all basic expenses and transfer this money in Spend-It account.
- If money is used before month end find the reasons and update your expenditure accordingly.
- In this way you will get idea about your expenditure in 2-3 months.
- Optimizing your expenditure :
- First find your expenditure.
- Apart from fixed cost, focus on your major 2 or 3 expenditure. eg : eating out, movies, clothes
- Track them and slowly try to decrease your spending in these areas.
- If all your expenses and saving goals are met you can allocate remaining money in guilt free money section.
- You don’t need to obsess over and track each minute change in your spending.
- Credit cards if used wisely can built your credit score. They provide reward points, consumer protection, concierge services etc.
- Credit cards to remember :
- Don’t get more than 3 credit cards
- Pay your credit cards bill regularly
- Tracking calls with financial companies. Use this table :
| Call date | Time | Name of rep | Rep’s ID # | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Building a Safety Net
Checklist :
- Build cash flow system
- Have emergency fund
- Get medical cover
-
Get life insurance
- Keep aside at least six months of living cost in FD’s , flexi FD’s, short term conservative mutual funds. This is the emergency fund.
Medical cover
- If your company don’t cover you post-retirement get your personal health insurance.
- You need a basic medical cover of Rs 3-15 lakhs per person.
- 3 lakh for small town and less posh facilities
- 15 lakh for metros
- Family floater medical cover is good for a nuclear family.
- Buying a right medical cover is hard. Choose medical cover by judging it on three metrices :
- How does it perform on the metric of price
- How does it perform on the metric of benefits
- How does it perform on the metric of claims(claim history)
- Look for these 8 things while choosing medical cover :
- No co-pay option
- Check for “pre-existing” disease clause
- Check if policy have ‘disease waiting period’
- Check for ‘sub-limits’
- Check for exclusions
- Ask how much of the costs before and after hospitalization the policy will cover
- Check details of ‘day care’ clause
- Look at ‘no-claims bonus’ feature
- Look for these things regarding claim history of medical policy
- How many claims does company settle? Should be atleast 95%
- Should have less than 30 complaints on every 10000 claims made
- Personal accident policy gives you a lump sum if you meet with an accident that leaves you temporarily or permanently disabled.
Life insurance
- You need life insurance cover of fifteen to twenty times your annualized monthly expenditure.
- You can also buy insurance for all the debts that you have.
- Buy insurance as soon as you have dependents(eg kids).
- Keep your insurance and investment separate. Don’t buy endowment plans, ULIPs. Get a term insurance plan.
- Look for claim experience of the term insurance before buying it.
- Don’t buy insurance if nobody will miss your income or you are financially independent.
- You are financially independent when your investments are large enough to look after your expenses.
- You can save tax by investing in PPF, NPS, ELSSs.
- Each financial product you buy solve a problem you have. It must have a purpose.
Understanding investment jargons
- Three asset classes : debt, equity, real assets(gold, real estate)
- Debt
- low risk, low return
- role is to provide money at short notice and to provide stability to your long-term investments.
- includes FDs, PPF, all the small savings products, bonds
- Disadvantages of buying real estate :
- Immobile, can be hard to sell
- Maintenance and other hidden charges which are ignored
- Not much return rate in long run
- Market capitalization = no. of shares * share price
- Large cap company : First 100 companies by market cap on the stock market. These are mature and established firms in market.
- Investment in equity needs ten years of patience to see consistent results. To get better results invest in equity for 15-20 years.
- Mid cap company : ranks between 101 to 250 by market cap.
- Small cap companies are rank 250 and below.
- Sensex is made up of 30 most representative companies listed in Bombay Stock Exchange(BSE).
- Similar to Sensex, there can be small cap index, mid cap index etc.
- When we say the Sensex went up, we mean that of the thirty companies in the Sensex more prices rose than fell.
- Average maturity : the average holding period of all the bonds is about three months. Some bonds may be maturing tomorrow, some in a week, some in two months and some may mature in four months.
- Asset allocation : dividing your investment into different asset classes depending on your investment horizon and risk tolerance.
Mutual Funds
- A mutual fund is a way to pool the money of a large number of small investors and hand it over to experts to manage it.
- 3 asset class of mutual funds :
- Equity : buy into stocks of listed companies
- Debt : buy bonds and debt papers issued by the government and firms
- Gold : buy actual gold
- Debt funds types :
- Liquid funds
- Ultra-short-term fund
- Liquid funds :
- Invest in bonds having average maturity of 3 months.
- keep money in a liquid fund if you know there is an expense coming up in the next three to six months.
- Ultra-short-term fund :
- Invest in bonds having average maturity of 9 months.
- invest in these if you need the money anytime in the next nine months to a year.
- Check that the top holdings of your debt fund is in AAA-rated bonds.
- Actively managed funds : Fund manager chooses which stocks to invest in.
- Passively managed funds : Buys stocks in indexes such as Sensex, Nifty50 etc.
- Equity funds types :
- Large cap
- Mid cap
- Small cap
- Growth option : Profit is reinvested into the fund.
- Dividend option : Profit is not reinvested and given as a periodic income.
- ELSS :
- Is an equity fund which gives tax benefits
- has a three-year lock-in period
- Balanced funds are hybrid funds. 3 types :
- Conservative : between 10 and 25 per cent in equity, rest in debt funds
- Balanced : between 40 and 60 per cent in equity
- Aggressive : about 65–80 per cent in equity
- Net asset value(NAV) : It is the price of a unit of a scheme. Multiply the NAV with the number of units you hold to get the value of your mutual fund holding per scheme.
- Expense ratio : cost of running and managing a mutual fund scheme. It is expressed in percentage terms.
- the difference between an expense ratio of 0.5 per cent and 1.5 per cent over a twenty-year period is huge.
- look at expense ratio of mutual fund you buy
- A 1 percent fee can reduce your returns by around 30 percent over thirty years.
- Systematic investment plan(SIP) : making periodic investments into a mutual fund.
- Systematic withdrawal plan (SWP) is a facility to periodically redeem your units to generate an income.
- Survivorship bias in Mutual fund performance :
- Funds that fail are not included in any future studies of fund performance for the simple reason that they don’t exist anymore.
- For example, a company may start a hundred funds but have only fifty left a couple of years later. The company can trumpet how effective their fifty funds are but ignore the fifty funds that failed and have been erased from history.
Mental Money Box
- Create a mental money box with following cells :
- Your cash flow
- Emergency fund
- Medical cover
- Life cover
- Almost there
- In some time
- Far Away
- Retirement
- Any planned expense that will happen within two to three years is a short-term need that you put down under Almost There. eg : Getting married, sending kid to school, buying a house, going for a holiday etc.
- In Some Time are planned expenses that sit between three to seven years away. eg : depending on age and stage marriage, retirement etc.
- Far Away are expenses that are really hard to imagine today and can be 30-50 years in future. This expense is for expenses other than retirement.
- Save your age At age twenty-five save 25 per cent of your post-tax income, at age thirty save 30 per cent of your post-tax income.
- At age sixty, you need between eighteen to thirty-five times your annual expenses at retirement to retire with the lifestyle you are used to.
- At age forty, you should have three times your annual income as your retirement corpus already
- Save about 10–15 per cent of your take-home salary towards your retirement.
Investing
- Investing isn’t about picking stocks. There is a difference between trading and investing.
- Most of the financial “experts” cannot reliably pick stocks that will outperform the market over the long term.
- The only long-term solution is to invest regularly, putting as much money as possible into low-cost, diversified funds, even in an economic downturn.
- Index funds are best way to get equity exposure.
- Asset allocation is the most significant part of your portfolio that you can control.
- Not more than 5–10 per cent of your total portfolio goes into gold. You do not buy jewellery as investment.
- Your options to buy gold are coins, bars, gold exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and gold bonds from the government.
- The thumb rule for equity is 100 minus your age. If you are thirty years old, you should have 70 per cent of your money in equity.
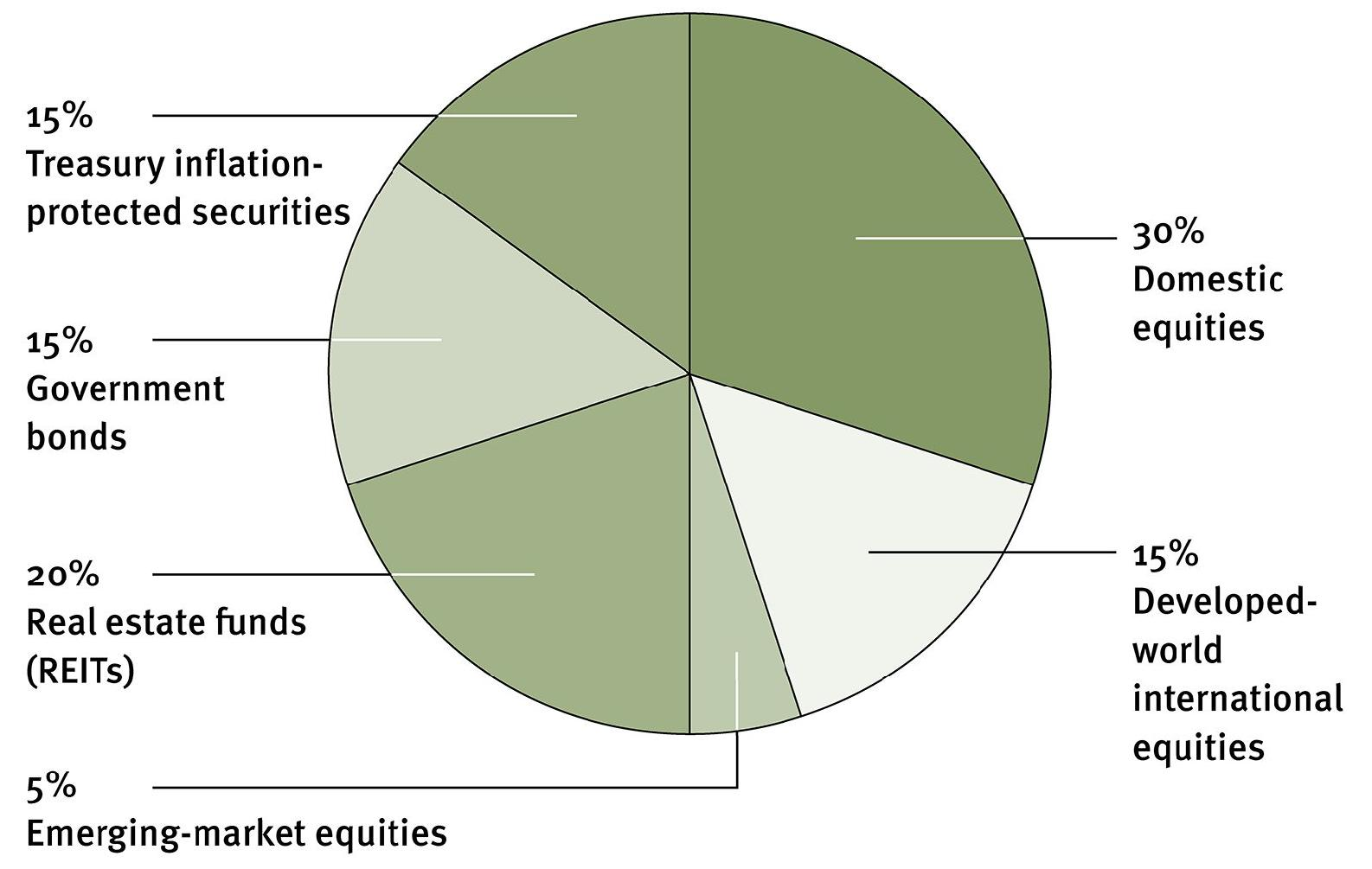
- Asset allocation as suggest by Swensen in I will teach you to be rich :
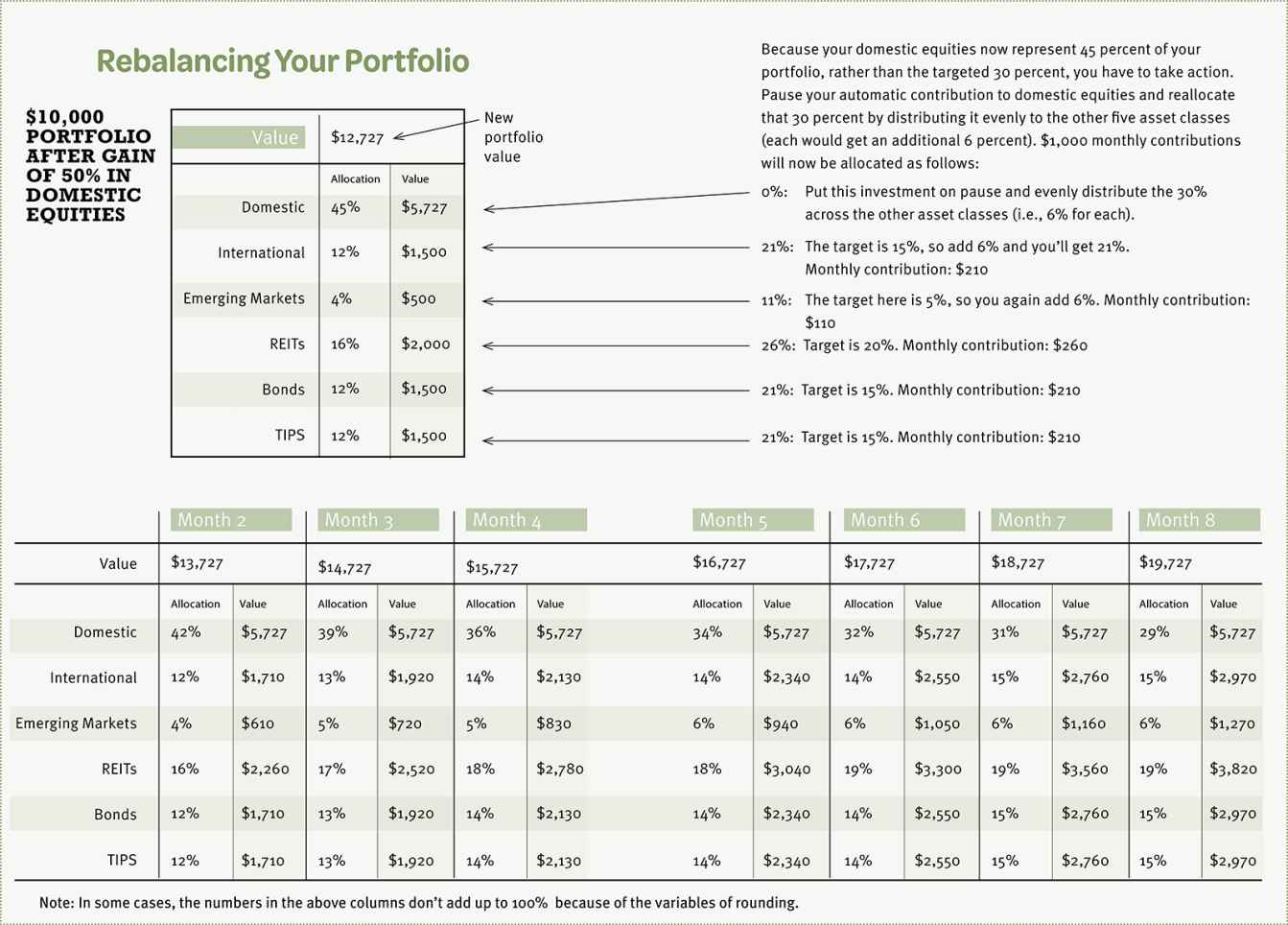
- Evaluate your investments atleast once a year and rebalance the portfolio if needed.
- Rebalancing your portfolio :